Amytal Sodium
Generic name:amobarbital sodium
Dosage form: injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution
Drug class:Barbiturates
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jul 1, 2020.
Disclaimer: This drug has not been found by FDA to be safe and effective, and this labeling has not been approved by FDA. Read further information about unapproved drugs.
On This Page
Amytal Sodium Description
The barbiturates are nonselective central nervous system (CNS) depressants that are primarily used as sedative hypnotics. In subhypnotic doses, they are also used as anticonvulsants. The barbiturates and their sodium salts are subject to control under the Federal Controlled Substances Act.
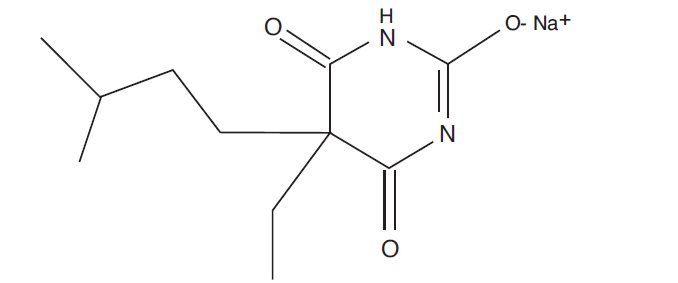
Amobarbital sodium is a white, friable, granular powder that is odorless, has a bitter taste, and is hygroscopic. It is very soluble in water, soluble in alcohol, and practically insoluble in ether and chloroform. Amobarbital sodium is sodium 5-ethyl-5-isopentylbarbiturate and has the empirical formula C11H17N2NaO3. Its molecular weight is 248.26.
It has the following structural formula:
Amobarbital sodium is a substituted pyrimidine derivative in which the basic structure is barbituric acid, a substance that has no CNS activity.
Vials of amobarbital sodium are for parenteral administration. The vials contain 500 mg (2 mmol) amobarbital sodium as a sterile lyophilized powder.
Amytal Sodium - Clinical Pharmacology
Barbiturates are capable of producing all levels of CNS mood alteration, from excitation to mild sedation, hypnosis, and deep coma. Overdosage can produce death. In high enough therapeutic doses, barbiturates induce anesthesia.
Barbiturates depress the sensory cortex, decrease motor activity, alter cerebellar function, and produce drowsiness, sedation, and hypnosis.
Barbiturate-induced sleep differs from physiologic sleep. Sleep laboratory studies have demonstrated that...