Mycostatin
Generic name:nystatin
Dosage form: Cream USP and Topical Powder USP
Drug class:Topical antifungals
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Mar 22, 2022.
FOR TOPICAL USE ONLY • NOT FOR OPHTHALMIC USE
On This Page
The Mycostatin Topical brand name has been discontinued in the U.S. If generic versions of this product have been approved by the FDA, there may be generic equivalents available.
Mycostatin Description
Nystatin is a polyene antifungal antibiotic obtained from Streptomyces nursei.
Structural formula:
Nystatin 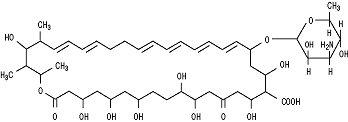
Mycostatin® Cream (Nystatin Cream) and Mycostatin® Topical Powder (Nystatin Topical Powder) are for dermatologic use.
Mycostatin® (Nystatin) Cream for topical use, contains 100,000 USP nystatin units per gram. Inactive ingredients: aluminum hydroxide concentrated wet gel, titanium dioxide, propylene glycol, cetearyl alcohol (and) ceteareth-20, white petrolatum, sorbitol solution, glyceryl monostearate, polyethylene glycol monostearate, sorbic acid and simethicone.
Mycostatin® (Nystatin) Topical Powder contains 100,000 USP nystatin units per gram dispersed in talc.
Mycostatin - Clinical Pharmacology
Pharmacokinetics
Nystatin is not absorbed from intact skin or mucous membrane.
Microbiology
Nystatin is an antibiotic which is both fungistatic and fungicidal in vitro against a wide variety of yeasts and yeast-like fungi, including Candida albicans, C. parapsilosis, C. tropicalis, C. guilliermondi, C. pseudotropicalis, C. krusei, Torulopsis glabrata, Tricophyton rubrum, T. mentagrophytes.
Nystatin acts by binding to sterols in the cell membrane of susceptible species resulting in a change in membrane permeability and the subsequent leakage of intracellular components. On repeated subculturing with increasing levels of nystatin, Candida albicans does not develop resistance to nystatin. Generally, resistance to nystatin does not develop during therapy. However, other species of Candida (



