Nuromax
Generic name: doxacurium chloride
Dosage form: injection
Drug class:Neuromuscular blocking agents
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 21, 2022.
This drug should be administered only by adequately trained individuals familiar with its actions, characteristics, and hazards.
On This Page
Nuromax Description
Nuromax (doxacurium chloride) is a long-acting, nondepolarizing skeletal muscle relaxant for intravenous administration. Doxacurium chloride is [1α,2β(1'S*,2'R*)]-2,2'-[(1,4-dioxo-1,4-butanediyl)bis(oxy-3,1-propanediyl)]bis[1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6,7,8-trimethoxy-2- methyl-1-[(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)methyl]isoquinolinium] dichloride (meso form). The molecular formula is C56H78CI2N2O16 and the molecular weight is 1106.14. The compound does not partition into the 1-octanol phase of a distilled water/ 1-octanol system, i.e., the n-octanol:water partition coefficient is 0.
Doxacurium chloride is a mixture of three trans, trans stereoisomers, a dl pair [(1R,1'R,2S,2'S) and (1S,1'S,2R,2'R)] and a meso form (1R,1'S,2S,2'R). The meso form is illustrated below:
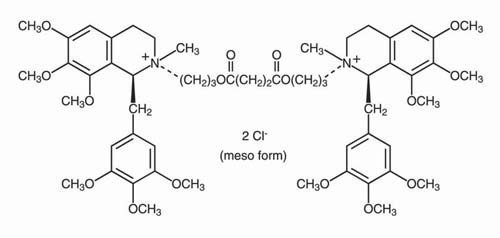
Nuromax Injection is a sterile, nonpyrogenic aqueous solution (pH 3.9 to 5.0) containing doxacurium chloride equivalent to 1 mg/mL doxacurium in Water for Injection. Hydrochloric acid may have been added to adjust pH. Nuromax Injection contains 0.9% w/v benzyl alcohol.
Nuromax - Clinical Pharmacology
Nuromax binds competitively to cholinergic receptors on the motor end-plate to antagonize the action of acetylcholine, resulting in a block of neuromuscular transmission. This action is antagonized by acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, such as neostigmine.
Pharmacodynamics
Nuromax is approximately 2.5 to 3 times more potent than...



