Pediapred Oral Solution
Generic name:prednisolone sodium phosphate
Dosage form: oral solution
Drug class:Glucocorticoids
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Dec 22, 2021.
On This Page
Pediapred Oral Solution Description
PEDIAPRED® (prednisolone sodium phosphate) Oral Solution is a dye free, colorless to light straw colored, raspberry flavored solution. Each 5 mL (teaspoonful) of PEDIAPRED® contains 6.7 mg prednisolone sodium phosphate (5 mg prednisolone base) in a palatable, aqueous vehicle. PEDIAPRED® also contains dibasic sodium phosphate, edetate disodium, methylparaben, purified water, sodium biphosphate, sorbitol, natural and artificial raspberry flavor. Prednisolone sodium phosphate occurs as white or slightly yellow, friable granules or powder. It is freely soluble in water; soluble in methanol; slightly soluble in alcohol and in chloroform; and very slightly soluble in acetone and in dioxane. The chemical name of prednisolone sodium phosphate is: pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione,11,17-dihydroxy-21-(phosphonooxy)-,disodium salt,(11β)-. The empirical formula is C21H27Na2O8P; the molecular weight is 484.39. Its chemical structure is:
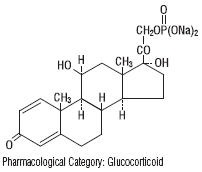
Pharmacological Category: Glucocorticoid
Pediapred Oral Solution - Clinical Pharmacology
Naturally occurring glucocorticoids (hydrocortisone), which also have salt-retaining properties, are used as replacement therapy in adrenocortical deficiency states. Their synthetic analogs are primarily used for their potent anti-inflammatory effects in disorders of many organ systems. Prednisolone is a synthetic adrenocortical steroid drug with predominantly glucocorticoid properties. Some of these properties reproduce the physiological actions of endogenous glucocorticosteroids, but others do not necessarily reflect any of the adrenal hormones’ normal functions; they are seen only after administration of large therapeutic doses of the drug. The pharmacological effects of prednisolone which are due to its glucocorticoid properties include: promotion of gluconeogenesis; increased deposition of glycogen in the liver; inhibition of the utilization of glucose; anti-insulin activity; increased catabolism of protein; increased lipolysis; stimulation of fat synthesis and storage; increased glomerular filtration rate and resulting increase in urinary...



