Sodium Phenylacetate and Sodium Benzoate Injection
Dosage form: injection
Drug class:Miscellaneous uncategorized agents
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Oct 1, 2021.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Use In Specific Populations
- Overdosage
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
Indications and Usage for Sodium Phenylacetate and Sodium Benzoate Injection
Sodium Phenylacetate and Sodium Benzoate Injection is indicated as adjunctive therapy in pediatric and adult patients for the treatment of acute hyperammonemia and associated encephalopathy in patients with deficiencies in enzymes of the urea cycle. During acute hyperammonemic episodes, arginine supplementation, caloric supplementation, dietary protein restriction, hemodialysis, and other ammonia lowering therapies should be considered [ see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
Sodium Phenylacetate and Sodium Benzoate Injection Dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosage
Sodium Phenylacetate and Sodium Benzoate Injection must be diluted with sterile 10% Dextrose Injection (D10W) before administration. The dilution and dosage of Sodium Phenylacetate and Sodium Benzoate Injection are determined by weight for neonates, infants and young children, and by body surface area for larger patients, including older children, adolescents, and adults (Table 1).
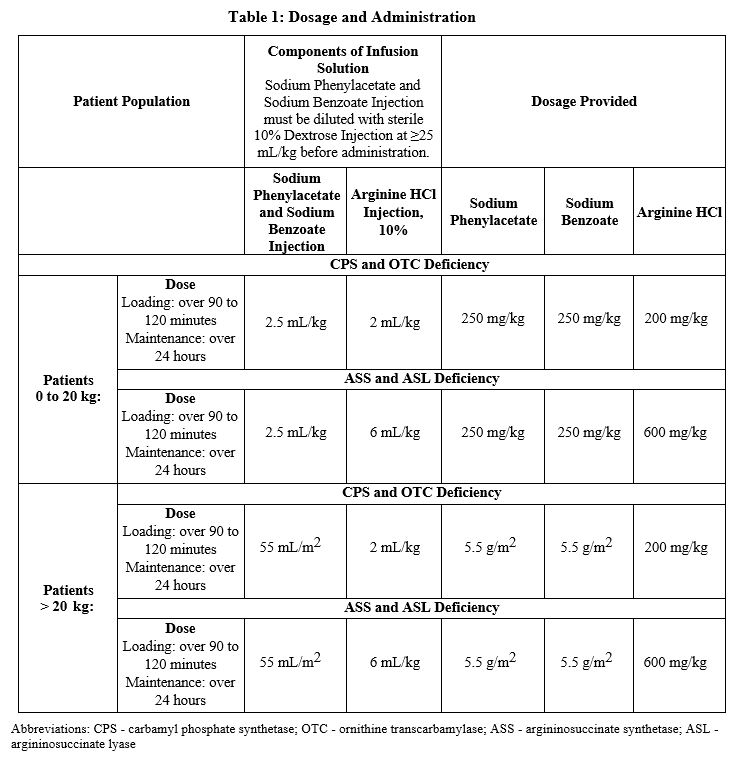
Administration
Sodium Phenylacetate and Sodium Benzoate Injection is a concentrated solution and must be diluted before intravenous administration via a central venous catheter. Administration through a peripheral intravenous catheter may cause burns. Sodium Phenylacetate and Sodium Benzoate Injection may not be administered by any other route.
Sodium Phenylacetate and Sodium Benzoate Injection should be administered as a loading dose infusion over 90 to 120 minutes, followed by the same dose repeated as a maintenance infusion administered over 24 hours. Because of prolonged plasma levels achieved by phenylacetate in pharmacokinetic studies, repeat loading doses of Sodium...



