Sodium Phenylbutyrate Powder
Dosage form: oral powder
Drug class:Urea cycle disorder agents
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jun 21, 2021.
On This Page
Sodium Phenylbutyrate Powder Description
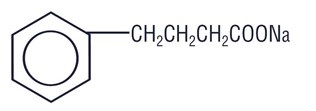
Sodium Phenylbutyrate Powder nasogastric, or gastrostomy tube administration contain sodium phenylbutyrate. Sodium Phenylbutyrate Powder is an off-white crystalline substance which is soluble in water and has a strong salty taste. Sodium phenylbutyrate also is freely soluble in methanol and practically insoluble in acetone and diethyl ether. It is known chemically as 4-phenylbutyric acid, sodium salt with a molecular weight of 186 and the molecular formula C10H11O2Na.
Chemical Structure:
Each gram of Sodium Phenylbutyrate Powder contains 0.94 grams of sodium phenylbutyrate and the inactive ingredients calcium stearate and colloidal silicon dioxide.
Sodium Phenylbutyrate Powder - Clinical Pharmacology
Sodium phenylbutyrate is a pro-drug and is rapidly metabolized to phenylacetate. Phenylacetate is a metabolically-active compound that conjugates with glutamine via acetylation to form phenylacetylglutamine. Phenylacetylglutamine then is excreted by the kidneys. On a molar basis, it is comparable to urea (each containing two moles of nitrogen). Therefore, phenylacetylglutamine provides an alternate vehicle for waste nitrogen excretion.
Pharmacokinetics
General:
Pharmacokinetic studies have not been conducted in the primary patient population (neonates, infants, and children), but pharmacokinetic data were obtained from normal adult subjects.
Absorption:
Peak plasma levels of phenylbutyrate occur within 1 hour after a single dose of 5 grams of Sodium Phenylbutyrate Powder with a Cmax of 195 mcg/mL under fasting conditions. The effect of food on phenylbutyrate's absorption is unknown.
Disposition:
The overall disposition of sodium phenylbutyrate and its metabolites has not been characterized fully. However, the drug is known to...



