Sodium Sulfacetamide and Sulfur Suspension
Dosage form: topical suspension
Drug class:Topical antibiotics
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 1, 2022.
Disclaimer: This drug has not been found by FDA to be safe and effective, and this labeling has not been approved by FDA. Read further information about unapproved drugs.
On This Page
For External Use Only. Not for Ophthalmic use.
Rx Only
Sodium Sulfacetamide and Sulfur Suspension Description
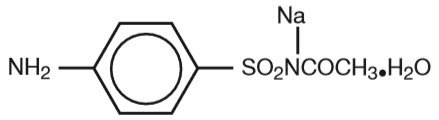
Sodium sulfacetamide is a sulfonamide with antibacterial activity while sulfur acts as a keratolytic agent. Chemically sodium sulfacetamide is N-[(4-aminophenyl) sulfonyl]-acetamide, monosodium salt, monohydrate. The structural formula is:
Each mL contains 90 mg of sodium sulfacetamide and 42.5 mg of sulfur in vehicle consisting of aloe vera gel, ammonium lauryl sulfate, butylated hydroxytoluene, cetyl alcohol, cocamidopropyl betaine, disodium EDTA, glycerin, glyceryl stearate SE, green tea extract, guar gum, methylparaben, PEG 100 stearate, propylene glycol, propylparaben, purified water, sodium thiosulfate, stearyl alcohol, and triacetin.
Sodium Sulfacetamide and Sulfur Suspension - Clinical Pharmacology
Sodium sulfacetamide exerts a bacteriostatic effect against sulfonamide sensitive Gram-positive and Gram-negative microorganisms commonly isolated from secondary cutaneous pyogenic infections. It acts by restricting the synthesis of folic acid required by bacteria for growth, by its competition with para-aminobenzoic acid. There is no clinical data available on the degree and rate of systemic absorption of this product when applied to the skin or scalp. However, significant absorption of sodium sulfacetamide through the skin has been reported.
The following in vitro data is available but the clinical significance is unknown. Organisms that show susceptibility to sodium sulfacetamide are: Streptococci, Staphylococci, E. coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas pyocyanea, Salmonella species, Proteus vulgaris, Nocardia and Actinomyces.
The exact mode of action of sulfur in the treatment of acne is unknown, but it has been reported that it inhibits the growth of Propionibacterium acnes and the formation of free fatty acids.



