Velosef
Generic name:Cephradine
Dosage form: capsule, suspension
Drug class:First generation cephalosporins
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Sep 21, 2021.
On This Page
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Velosef and other antibacterial drugs, Velosef should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria.
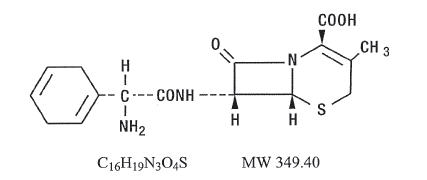
Velosef Description
Velosef (Cephradine) is a semisynthetic cephalosporin antibiotic; oral dosage forms include capsules containing 250 mg and 500 mg cephradine and cephradine for oral suspension containing, after constitution, 125 mg and 250 mg per 5 mL dose.
Cephradine is designated chemically as (6R, 7R)-7-[(R)-2-amino-2-(1,4-cyclohexadien-1-yl)acetamido]-3-methyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid. Structural formula:
Inactive ingredients: Velosef Capsules—colorants (D&C Red No. 33 and Yellow No. 10; FD&C Blue No. 1, and, for ‘250’ only, Red No. 3), gelatin, lactose, magnesium stearate, talc, and titanium dioxide. Velosef for Oral Suspension—citric acid, colorants (FD&C Red No. 40 for ‘250’ only; FD&C Yellow No. 6 for ‘125’ only), flavors, guar gum, methylcellulose, sodium citrate, and sucrose.
Velosef - Clinical Pharmacology
Velosef (Cephradine) is acid stable. It is rapidly absorbed after oral administration in the fasting state. Following single doses of 250 mg, 500 mg, and 1 g in normal adult volunteers, average peak serum concentrations within one hour were approximately 9 mcg/mL, 16.5 mcg/mL, and 24.2 mcg/mL, respectively. In vitro studies by an ultracentrifugation technique show that at therapeutic serum antibiotic concentrations, cephradine is minimally bound (8 to 17 percent) to normal serum protein. Cephradine does not pass across the blood-brain barrier to any appreciable extent. The presence of food in the gastrointestinal tract delays absorption but does not affect the total amount of cephradine absorbed. Over 90 percent of the drug is excreted unchanged in the urine within six hours. Peak urine concentrations are approximately 1600 mcg/mL, 3200 mcg/mL, and 4000 mcg/mL following single doses of 250 mg, 500 mg, and 1 g, respectively.



