BACiiM
Generic name:bacitracin
Dosage form: injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution
Drug class:Miscellaneous antibiotics
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Dec 22, 2021.
On This Page
Nephrotoxicity: Bacitracin in parenteral (intramuscular) therapy may cause renal failure due to tubular and glomerular necrosis. Its use should be restricted to infants with staphylococcal pneumonia and empyema when due to organisms shown to be susceptible to bacitracin. It should be used only where adequate laboratory facilities are available and when constant supervision of the patient is possible.
Renal function should be carefully determined prior to and daily during therapy. The recommended daily dose should not be exceeded and fluid intake and urinary output should be maintained at proper levels to avoid kidney toxicity. If renal toxicity occurs the drug should be discontinued. The concurrent use of other nephrotoxic drugs, particularly streptomycin, kanamycin, polymyxin B, polymyxin E (colistin), neomycin, and vancomycin, should be avoided.
DESCRIPTION
Bacitracin for Injection, USP is a sterile antibiotic for intramuscular administration. Bacitracin is derived from cultures of Bacillus subtilis (Tracey). It is a white to pale buff, hygroscopic powder, odorless or having a slight odor. It is freely soluble in water; insoluble in acetone, chloroform, and ether. While soluble in alcohol, methanol, and glacial acetic acid, there is some insoluble residue. It is precipitated from its solutions and inactivated by many of the heavy metals.
Each vial contains 50,000 units of bacitracin.
The structural formula is:
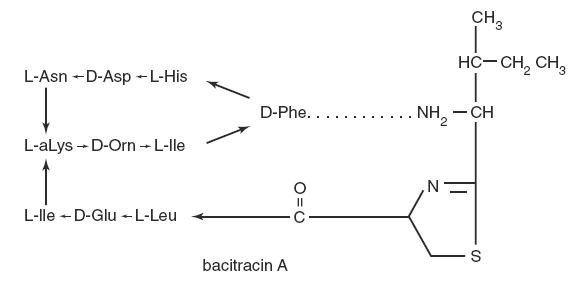
baci-molecular
The molecular formula is: C66H103N17O16S
Bacitracin is comprised of a polypeptide complex and Bacitracin A is the major component in this complex. The molecular weight of Bacitracin A is 1422.71.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Bacitracin exerts pronounced antibacterial action in vitro<...



