Vivacaine
Generic name:bupivacaine hydrochloride and epinephrine bitartrate
Dosage form: injection, solution
Drug class:Local injectable anesthetics
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jun 1, 2021.
On This Page
Rx only
THIS SOLUTION IS INTENDED FOR DENTAL USE.
Vivacaine Description
Bupivacaine hydrochloride is (±) -1-Butyl-2´, 6´-pipecoloxylidide monohydrochloride, monohydrate, a white crystalline powder that is freely soluble in 95 percent ethanol, soluble in water, and slightly soluble in chloroform or acetone. It has the following structural formula:
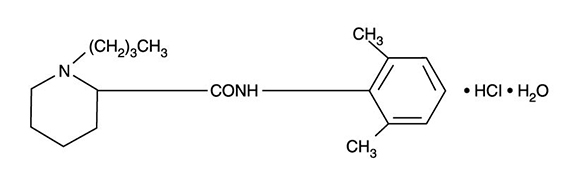 Molecular Weight - 342.90 C18 H28 N2O • HCl • H2O
Molecular Weight - 342.90 C18 H28 N2O • HCl • H2O
Epinephrine bitartrate is (-)-1-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-2-methylamino-ethanol (+) tartrate (1:1) salt. It has the following structural formula:
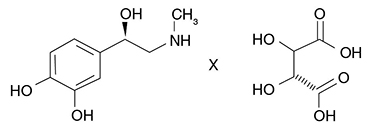 Molecular Weight - 333.29 C13H19NO9
Molecular Weight - 333.29 C13H19NO9
Bupivacaine is available in a sterile isotonic solution with epinephrine 1:200,000 (as bitartrate). Solutions of bupivacaine containing epinephrine may not be autoclaved.
Bupivacaine is related chemically and pharmacologically to the aminoacyl local anesthetics. It is a homologue of mepivacaine and is chemically related to lidocaine. All three of these anesthetics contain an amide linkage between the aromatic nucleus and the amino or piperidine group. They differ in this respect from the procaine-type local anesthetics, which have an ester linkage.
Vivacaine - Clinical Pharmacology
Bupivacaine stabilizes the neuronal membrane and prevents the initiation and transmission of nerve impulses, thereby effecting local anesthesia.
The onset of action following dental injections is usually 2 to 10 minutes and anesthesia may last two or three times longer than lidocaine and mepivacaine for dental use, in many patients up to 7 hours. The duration of anesthetic effect is prolonged by the addition of epinephrine 1:200,000.
It has also been noted that th...



