Chloroprocaine
Generic name: Chloroprocaine hydrochloride
Dosage form: injection, solution
Drug class:Local injectable anesthetics
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Feb 1, 2022.
On This Page
Rx ONLY
Chloroprocaine Description
Chloroprocaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP is a sterile non-pyrogenic local anesthetic. The active ingredient is Chloroprocaine HCl (benzoic acid, 4-amino-2-chloro-2-(diethylamino) ethyl ester, monohydrochloride), which is represented by the following structural formula:
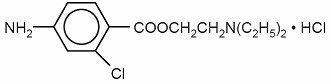
Molecular Formula: C13H19ClN2O2 • HCl M. W. 307.22
Chloroprocaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP is available in a 2% and 3% solution for infiltration, nerve block, caudal and epidural anesthesia (not for spinal anesthesia).
Each mL of the 20 mg/mL, 2%, solution contains; 20 mg of Chloroprocaine HCl, USP, 4.7 mg of Sodium Chloride, USP, and Sodium Hydroxide and/or Hydrochloric Acid to adjust pH. The pH range is 2.7 to 4.0.
Each mL of the 30 mg/mL, 3%, solution contains; 30 mg of Chloroprocaine HCl, USP, 3.3 mg of Sodium Chloride, USP, and Sodium Hydroxide and/or Hydrochloric Acid to adjust pH. The pH range is 2.7 to 4.0.
Chloroprocaine HCl Injection, USP, should not be resterilized by autoclaving.
Chloroprocaine - Clinical Pharmacology
Chloroprocaine, like other local anesthetics, blocks the generation and the conduction of nerve impulses, presumably by increasing the threshold for electrical excitation in the nerve, by slowing the propagation of the nerve impulse and by reducing the rate of rise of the action potential. In general, the progression of anesthesia is related to the diameter, myelination and conduction velocity of affected nerve fibers. Clinically, the order of loss of nerve function is as follows: (1) pain, (2) temperature, (3) touch, (4) proprioception, and (5) skeletal muscle tone.
Systemic absorption of local anesthetics produces effects on the cardiovascular and ...



