Etidronate
Generic name: Etidronate disodium
Dosage form: tablet
Drug class:Bisphosphonates
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Feb 21, 2022.
On This Page
Etidronate Description
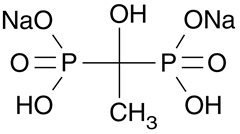
Etidronate disodium tablets, USP contain either 200 mg or 400 mg of Etidronate disodium, the disodium salt of (1-hydroxyethylidene) diphosphonic acid, for oral administration. This compound, also known as EHDP, regulates bone metabolism. Etidronate disodium, USP is a white powder, highly soluble in water, with a molecular weight of 250 and the following structural formula:
Inactive ingredients: Each tablet contains magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, pregelatinized starch and starch (corn).
Etidronate - Clinical Pharmacology
Etidronate disodium acts primarily on bone. It can inhibit the formation, growth, and dissolution of hydroxyapatite crystals and their amorphous precursors by chemisorption to calcium phosphate surfaces. Inhibition of crystal resorption occurs at lower doses than are required to inhibit crystal growth. Both effects increase as the dose increases.
Etidronate disodium is not metabolized. The amount of drug absorbed after an oral dose is approximately 3%. In normal subjects, plasma half-life (t1/2) of Etidronate, based on non-compartmental pharmacokinetics is 1 to 6 hours. Within 24 hours, approximately half the absorbed dose is excreted in urine; the remainder is distributed to bone compartments from which it is slowly eliminated. Animal studies have yielded bone clearance estimates up to 165 days. In humans, the residence time on bone may vary due to such factors as specific metabolic condition and bone type. Unabsorbed drug is excreted intact in the feces. Preclinical studies indicate Etidronate disodium does not cross the blood-brain barrier.
Etidronate disodium therapy does not adversely affect serum levels of parathyroid hormone or calcium.
Paget’s Disease
Paget’s disease of bone (osteitis deformans) is an idiopathic, progressive disease characterized by abnormal and accelerated bone metabolism in one or more bones. Signs and symptoms may include bone pain and/or deformity, neurologic disorders, elevated cardi...