Fossaoprin SPG4 Injection System
Generic name: lidocaine hydrochloride, bupivacaine hydrochloride
Dosage form: kit
On This Page
LIDOCAINE HYDROCHLORIDE- lidocaine hydrochloride injection, solution
Rx only
1.1 DESCRIPTION
4% Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution containing lidocaine hydrochloride, anhydrous 40 mg/mL in water for injection. May contain sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid for pH adjustment. pH 6.5 (5.0 to 7.0).
Lidocaine has cardiac antiarrhythmic properties and is a local anesthetic of the amide type.
Lidocaine Hydrochloride, USP is chemically designated 2-(diethylamino)-2′,6′-acetoxylidide monohydrochloride monohydrate, a white powder freely soluble in water. It has the following structural formula:
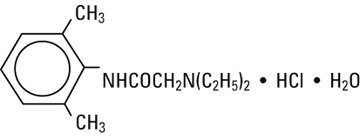
1.2 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of action: Lidocaine stabilizes the neuronal membrane by inhibiting the ionic fluxes required for the initiation and conduction of impulses, thereby effecting local anesthetic action.
Onset and duration of anesthesia: The onset of action is rapid. For retrobulbar injection, 4 mL of 4% Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP provides an average duration of action of 1 to 1½ hours. This duration may be extended for ophthalmic surgery by the addition of epinephrine, the usual recommended dilution being 1:50,000 to 1:100,000.
Hemodynamics: Excessive blood levels may cause changes in cardiac output, total peripheral resistance, and mean arterial pressure. These changes may be attributable to a direct depressant effect of the local anesthetic agent on various components of the cardiovascular system. The net effect is normally a modest hypotension when the recommended dosages are not exceeded.
Pharmacokinetics and metabolism: Information derived from other formulations, concentrations and usages reveals that lidocaine is completely absorbed following parenteral administration, its rate of absorption depending, for example, upon such factors such as the site of administration and the presence or absence of a vasoconstrictor agent. Lidocaine may be absorbed following topical administration to mucous membranes, its rate and extent of absorption depending upon concentration and total dose administered, the sp...



