Inamrinone
Dosage form: injection
Drug class:Inotropic agents
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Dec 22, 2021.
On This Page
Rx ONLY.
Sterile Intravenous Solution
Inamrinone Description
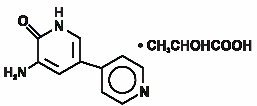
Inamrinone Injection USP represents a new class of cardiac inotropic agents distinct from digitalis glycosides or catecholamines. Inamrinone lactate is designated chemically as 5-Amino[3,4'-bipyridin]-6(1H)-one 2-hydroxypropanate and has the following structure:
Inamrinone is a pale yellow crystalline compound with a molecular weight of 187.20 and a molecular formula of C10H9N3O. Each mole of lactic acid has a molecular weight of 90.08 and a empirical formula of C3H6O3. The solubilities of Inamrinone at pH’s 4.1, 6.0, and 8.0 are 25, 0.9, and 0.7 mg/mL, respectively.
Inamrinone injection is a clear yellow sterile solution available in 20 mL vials for intravenous administration. Each mL contains Inamrinone lactate equivalent to 5 mg of Inamrinone and 0.25 mg of sodium metabisulfite added as a preservative in Water for Injection. All dosages expressed in the package insert are expressed in terms of the base, Inamrinone. The pH is adjusted to between 3.2 to 4.0 with lactic acid or sodium hydroxide. The total concentration of lactic acid can vary between 5 mg and 7.5 mg.
Inamrinone - Clinical Pharmacology
Inamrinone is a positive inotropic agent with vasodilator activity, different in structure and mode of action from either digitalis glycosides or catecholamines.
The mechanism of its inotropic and vasodilator effects has not been fully elucidated.
With respect to its inotropic effect, experimental evidence indicates that it is not a beta-adrenergic agonist. It inhibits myocardial cyclic adenosine monophosphate (c-AMP) phosphodiesterase activity and increases cellular levels of c-AMP. Unlike digitalis, it does not inhibit sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphatase activity.
With respect to its vasodilatory activity, Inamrinone reduces afterloa...