Isuprel
Generic name:isoproterenol hydrochloride
Dosage form: injection, solution
Drug classes:Adrenergic bronchodilators, Catecholamines, Vasopressors
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 1, 2020.
On This Page
Isoproterenol Hydrochloride Injection, USP
Sterile Injection
Rx only
DESCRIPTION
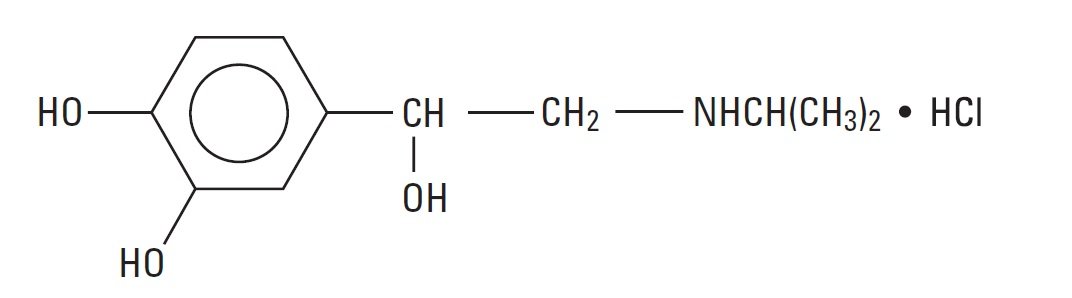
Isoproterenol hydrochloride is 3,4-Dihydroxy-α-[(isopropylamino)methyl] benzyl alcohol hydrochloride, a synthetic sympathomimetic amine that is structurally related to epinephrine but acts almost exclusively on beta receptors. The molecular formula is C11H17NO3 ● HCl. It has a molecular weight of 247.72 and the following structural formula:
Isoproterenol hydrochloride is a racemic compound.
Each milliliter of the sterile solution contains:
- Isoproterenol hydrochloride injection, USP 0.2 mg
Edetate Disodium (EDTA) 0.2 mg
Sodium Chloride 7.0 mg
Sodium Citrate, Dihydrate 2.07 mg
Citric Acid, Anhydrous 2.5 mg
Water for Injection 1.0 mL
The pH is adjusted between 3.5 and 4.5 with hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide.
The sterile solution is nonpyrogenic and can be administered by the intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous or intracardiac routes.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Isoproterenol is a potent nonselective beta-adrenergic agonist with very low affinity for alpha-adrenergic receptors. Intravenous infusion of isoproterenol in man lowers peripheral vascular resistance, primarily in skeletal muscle but also in renal and mesenteric vascular beds. Diastolic pressure falls. Renal blood flow is decreased in normotensive subjects but is increased markedly in shock. Systolic blood pressure may remain unchanged or rise, although mean arterial pressure typically falls. Cardiac output is increased because of the positive inotropic and chronotropic effects of the drug in the face of diminished peripheral vascular resistance. The cardiac effects of isoproterenol may lead to palp