Jeanatope
Generic name: iodinated i-125 albumin
Dosage form: injection, solution
On This Page
Rx Only.
Jeanatope Description
Jeanatope I-125 (Iodinated I-125 Albumin Injection) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic, aqueous solution for intravenous use. Each milliliter provides approximately 10 mg protein (normal human serum albumin), 16 mg dibasic sodium phosphate, 1.6 mg monobasic sodium phosphate, not more than 0.4 mg guanidine hydrochloride, sodium chloride for isotonicity, and 9 mg benzyl alcohol as a preservative. The pH has been adjusted to 7.2-7.8 with sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid.
Jeanatope I-125 was prepared from blood that was nonreactive when tested for hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) and HIV antibody.
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Iodine 125 decays by electron capture with a physical half-life of 60.14 days.1 Photons that are useful for detection and imaging studies are listed in Table 1.
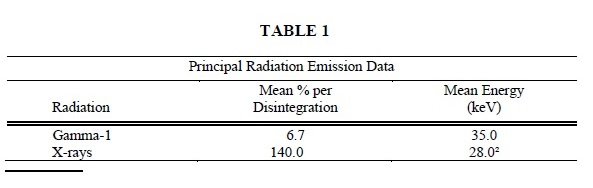
1 Dillman LT, Von der Lage FC; Radionuclide Decay Schemes and Nuclear Parameters for Use in Radiation-Dose Estimation. MIRD Pamphlet No. 10, pg.71 Soc Nucl Med, 1975.
² Weighted mean energy
External Radiation
The specific gamma ray constant for I-125 is 1.5 R/millicurie-hour at 1 cm. The first half-value thickness of Pb for I-125 is .002 mm. A range of values for the relative attenuation of the radiation emitted by this radionuclide that results from interposition of various thicknesses of Pb is shown in Table 2. For example, the use of .02 mm of Pb will decrease the external radiation exposure by a factor of 1,000.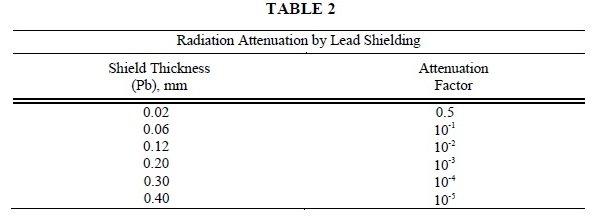
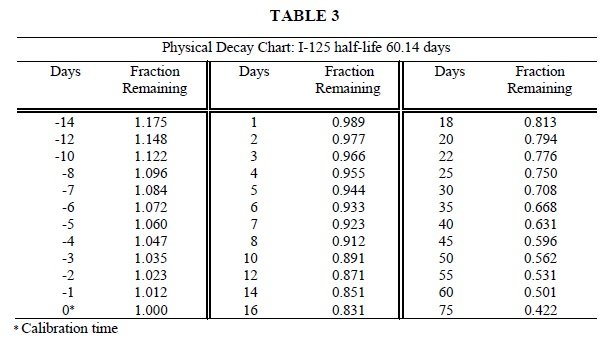
To correct for physical decay of this radionuclide, the fractions that remain at selected intervals before and after the time of calibration are shown in Table 3.
Jeanatope - Clinical Pharmacology
Following intravenous injection, radioiodinated serum albumin is uniformly distributed throughout the intravascular pool within 10 minutes; extravascular distribution takes place more slowly. Labeled albumin also can be detected in the lymph and in certain body tissues within 10 minutes after injection, but maximum distribution of radioactivity throughout the extravascular space does not occur until two to fo.



