Aminocaproic
Generic name: Aminocaproic acid
Dosage form: tablet
Drug class:Miscellaneous coagulation modifiers
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jan 1, 2022.
On This Page
Aminocaproic Description
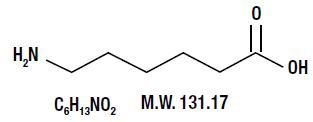
Aminocaproic acid is 6-aminohexanoic acid, which acts as an inhibitor of fibrinolysis.
Its chemical structure is:
Aminocaproic acid, USP is a fine, white to almost white, crystalline powder. It is freely soluble in water, in acids, and in alkaline solutions; it is slightly soluble in methanol and practically insoluble in chloroform and in ether.
Each Aminocaproic acid tablet, USP for oral administration contains 500 mg of Aminocaproic acid, USP and the following inactive ingredients: crospovidone type B, magnesium stearate, povidone and stearic acid.
Meets USP Dissolution Test 2.
Aminocaproic - Clinical Pharmacology
The fibrinolysis-inhibitory effects of Aminocaproic acid appear to be exerted principally via inhibition of plasminogen activators and to a lesser degree through antiplasmin activity.
In adults, oral absorption appears to be a zero-order process with an absorption rate of 5.2 g/hr. The mean lag time in absorption is 10 minutes. After a single oral dose of 5 g, absorption was complete (F=1). Mean ± SD peak plasma concentrations (164 ± 28 mcg/mL) were reached within 1.2 ± 0.45 hours.
After oral administration, the apparent volume of distribution was estimated to be 23.1 ± 6.6 L (mean± SD). Correspondingly, the volume of distribution after intravenous administration has been reported to be 30.0 ± 8.2 L. After prolonged administration, Aminocaproic acid has been found to distribute throughout extravascular and intravascular compartments of the body, penetrating human red blood cells as well as other tissue cells.
Renal excretion is the primary route of elimination. Sixty-five percent of the dose is recovered in the urine as unchanged drug and 11% of the dose appears as the metabolite adipic acid. Renal clearance (116 mL/min) approximates endogenous creatinine clearance. The total body clearance is 169 mL/min. The terminal elimination half-life for Aminocaproic acid is approximately 2 hours.