Levobunolol
Generic name: Levobunolol hydrochloride
Dosage form: ophthalmic solution
Drug class:Ophthalmic glaucoma agents
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jul 22, 2021.
On This Page
Rx only
FOR USE IN THE EYES ONLY
Description:
Levobunolol Hydrochloride Ophthalmic Solution, USP 0.5% is a noncardioselective beta-adrenoceptor blocking agent for ophthalmic use.
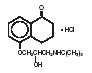
Levobunolol hydrochloride is represented by the following structural formula:
C17H25NO3•HCl
Mol. Wt. 327.85
Chemical Name: (-)-5-[3-(tert-Butylamino)-2-hydroxypropoxy]-3,4-dihydro-1(2H)-naphthalenone hydrochloride.
Each mL of 0.5% contains:
ACTIVE: Levobunolol Hydrochloride 0.5%; INACTIVES: Polyvinyl Alcohol 1.4%, Sodium Chloride, Dibasic Sodium Phosphate, Edetate Disodium, Sodium Metabisulfite, Monobasic Potassium Phosphate, and Purified Water. Hydrochloric Acid and/or Sodium Hydroxide may be added to adjust pH (5.5 - 7.5); PRESERVATIVE: Benzalkonium Chloride (0.004%).
Clinical Pharmacology:
Levobunolol hydrochloride is a noncardioselective beta-adrenoceptor blocking agent, equipotent at both beta1 and beta2 receptors. Levobunolol hydrochloride is greater than 60 times more potent than its dextro isomer in its beta-blocking activity, yet equipotent in its potential for direct myocardial depression. Accordingly, the levo isomer, Levobunolol hydrochloride, is used. Levobunolol hydrochloride does not have significant local anesthetic (membrane-stabilizing) or intrinsic sympathomimetic activity.
Beta-adrenergic receptor blockade reduces cardiac output in both healthy subjects and patients with heart disease. In patients with severe impairment of myocardial function, beta-adrenergic receptor blockade may inhibit the stimulatory effect of the sympathetic nervous system necessary to maintain adequate cardiac function.
Beta-adrenergic receptor blockade in the bronchi and bronchioles results in increased airway resistance from unopposed parasympathetic activity. Such an effect in patients with asthma or other bronchospastic co...