Lidorex Gel
Generic name:lidocaine hydrochloride
Dosage form: gel
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Oct 1, 2021.
Disclaimer: This drug has not been found by FDA to be safe and effective, and this labeling has not been approved by FDA. Read further information about unapproved drugs.
On This Page
Lidorex Gel Description
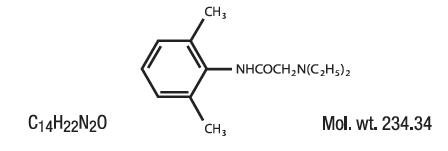
Contains Lidocaine HCl 2.8% in a mild acidic vehicle. Lidocaine is chemically designated as acetamide, 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl), and has the following structure:
INGREDIENTS: Each gram of Lidorex™ 2.8% Gel contains Lidocaine HCl USP 28 mg. Inactive Ingredients include: Aloe Barbadensis (Aloe Vera) Leaf Juice, Citric Acid, Hydroxyethylcellulose, Methylparaben, PEG-4, Propylene Glycol, Propylparaben, Purified Water.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY:
MECHANISM OF ACTION:
Lidorex™ 2.8% Gel releases Lidocaine from a mild acidic vehicle to stabilize the neuronal membrane by inhibiting the ionic fluxes required for initiation and conduction of impulses, thereby affecting local anesthetic action. A mild acidic vehicle lowers pH to increase protection against alkaline irritants and to provide a favorable environment for healing.
PHARMACOKINETICS:
Lidocaine may be absorbed following topical administration to mucous membranes, its rate and extent of absorption depending upon the specific site of application, duration of exposure, concentration, and total dosage. In general, the rate of absorption of local anesthetic agents following topical application occurs most rapidly after intratracheal administration. Lidocaine is also well-absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, but little intact drug appears in the circulation because of biotransformation in the liver.
Lidocaine is metabolized rapidly by the liver and metabolites and unchanged drugs are excreted by the kidneys. Biotransformation includes oxidative N-dealkylation, ring hydroxylation, cleavage of the amide linkage, and conjugation. N-dealkylation, a major pathway of biotransformation, yields the metabolites monoethylglycinexylidide and glycinexylidide. The pharmacological/toxicological actions of these metabolites are similar to but less potent than, those of Lidocaine. Approximate...



