Maxaquin
Generic name:lomefloxacin hydrochloride
Dosage form: Tablets
Drug class:Quinolones
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 21, 2022.
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Maxaquin and other antibacterial drugs, Maxaquin should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria.
On This Page
Maxaquin Description
Maxaquin (lomefloxacin HCl) is a synthetic broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent for oral administration. Lomefloxacin HCl, a difluoroquinolone, is the monohydrochloride salt of (±)-1-ethyl-6,8-difluoro-1,4-dihydro-7-(3-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid. Its empirical formula is C17H19F2N3O3•HCl, and its structural formula is:
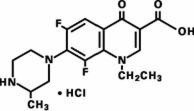
Lomefloxacin HCl is a white to pale yellow powder with a molecular weight of 387.8. It is slightly soluble in water and practically insoluble in alcohol. Lomefloxacin HCl is stable to heat and moisture but is sensitive to light in dilute aqueous solution.
Maxaquin is available as a film-coated tablet formulation containing 400 mg of lomefloxacin base, present as the hydrochloride salt. The base content of the hydrochloride salt is 90.6%. The inactive ingredients are carboxymethylcellulose calcium, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, lactose, magnesium stearate, polyethylene glycol, polyoxyl 40 stearate, and titanium dioxide.
Maxaquin - Clinical Pharmacology
Pharmacokinetics in healthy volunteers
In 6 fasting healthy male volunteers, approximately 95% to 98% of a single oral dose of lomefloxacin was absorbed. Absorption was rapid following single doses of 200 and 400 mg (Tmax 0.8 to 1.4 hours). Mean plasma concentration increased proportionally between 100 and 400 mg as shown below:



