MD-Gastroview
Generic name:diatrizoate meglumine and diatrizoate sodium
Dosage form: oral and rectal solution
Drug class:Ionic iodinated contrast media
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jan 1, 2021.
On This Page
MD-Gastroview Description
MD-Gastroview (Diatrizoate Meglumine and Diatrizoate Sodium Solution) is a palatable lemon-vanilla flavored water-soluble iodinated radiopaque contrast medium for oral or rectal administration only. Each mL contains 660 mg diatrizoate meglumine and 100 mg diatrizoate sodium; pH has been adjusted to 6.0 to 7.6 with sodium hydroxide. Each mL contains approximately 4.8 mg (0.21 mEq) sodium and 367 mg organically bound iodine. MD-Gastroview does not contain the wetting agent polysorbate 80.
The inactive ingredients are: Edetate Disodium Dihydrate, Lemon-Vanilla Flavor, Sodium Citrate, Sodium Hydroxide, Sodium Saccharin, Water for Injection. Air in the container is displaced with nitrogen.
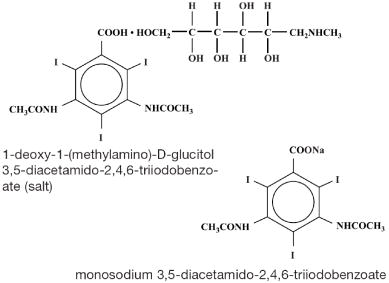
Diatrizoate meglumine is designated chemically as 1-deoxy-1-(methylamino)-D-glucitol 3,5-diacetamido-2,4,6-triiodobenzoate (salt); diatrizoate sodium is monosodium 3,5-diacetamido-2,4,6-triiodobenzoate. The two salts have the following structural formulae:
MD-Gastroview - Clinical Pharmacology
The most important characteristic of contrast media is the iodine content. The relatively high atomic weight of iodine contributes sufficient radiodensity for radiographic contrast with surrounding tissues.
Diagnostic enteral radiopaque agents have few known pharmacological effects. Diatrizoate meglumine and diatrizoate sodium exert a mild laxative effect attributable to their high osmolarity.
Diatrizoate meglumine and diatrizoate sodium are sparingly absorbed from the intact gastrointestinal tract, and therefore permit gastrointestinal opacification and delineation after oral or rectal administration. Oral administration is used for radiographic evaluation of the esophagus, stomach and proximal small intestine. Rectal administration is used for examination of the colon; however, visualization of the distal small bowel is generally unsatisfactory, since the hypertonicity of the medium causes intraluminal diffusion of water with subsequent dilution of the medium. Enough absorption fro...



