Megatope
Generic name: iodinated i-131 albumin
Dosage form: injection, solution
Drug class:Diagnostic radiopharmaceuticals
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 23, 2022.
On This Page
CAUTION
Federal (USA) law prohibits dispensing without prescription
Megatope Description
Megatope (Iodinated I 131 Albumin Injection) is a diagonostic radiopharmaceutical
containing iodinated I 131 albumin for intravenous use. Each mL of sterile, nonpyro-
genic, aqueous, colorless to very pale yellow solution provides approximate 10 mg
protein (albumin human), 16 mg dibasic sodium phosphate, 1.6 mg monobasic
sodium phosphate, not more than 0.4 guanidine hydrochloride, sodium chloride
for isotonicity, and 9 mg benzyl alcohol as a preservative. The pH has been adjusted
to 7.2 to 7.8 with sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid.
Megatope was prepared from blood that was nonreactive when tested for hepatitis
B surface antigen (HBsAg).
The structure of the complex is unknown.
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS
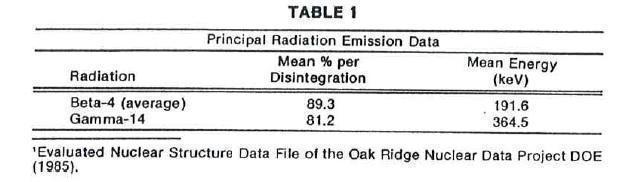
Iodine 131 decays by beta and gamma emissions with a physical half-life of 8.08 days.1
Photons that are useful for detection and imaging studies are listed in Table 1.
External Radiation
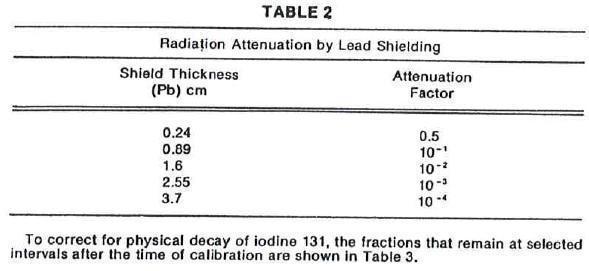
The specific gamma ray constant for iodine 131 is 2.2 R/hour-millicurie at 1 cm. The
first half-value layer is 0.24 cm lead (Pb). A range of values for the relative attenuation
of the radiation emitted by this radionuclide that result from interposition of various
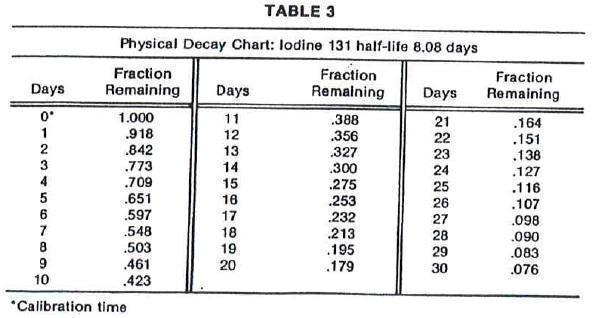
thicknesses of Pb is shown in Table 2. To facilitate control of the radiation exposure
from this radionuclide, the use of a 2.55 cm thickness of Pb will attenuate the radiation
emitted by a factor of about 1,000.
Megatope - Clinical Pharmacology
Following intravenous injection, radioiodinated albumin human is uniformly
distributed throughout the intravascular pool within 10 minutes; extravascular
distribution takes place more slowly. Iodinated I 131 albumin can also be detected in



