Methocarbamol and Aspirin Tablet
Dosage form: tablet
Drug class:Skeletal muscle relaxant combinations
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Mar 1, 2021.
On This Page
DESCRIPTION
Each tablet, for oral administration contains:
Methocarbamol, USP 400 mg
Aspirin, USP 325 mg
Inactive Ingredients: Pregelatinized starch, povidone, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium starch glycolate, colloidal silicon dioxide, stearic acid.
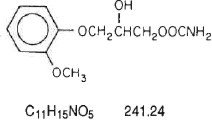
The chemical name of methocarbamol is 3-(2-meth-oxyphenoxy)-1,2-propanediol 1-carbamate and has the chemical formula C11H15NO5. Its molecular weight is 241.24. Methocarbamol is a white powder, sparingly soluble in water and chloroform, soluble in alcohol (only with heating) and propylene glycol, and insoluble in benzene and n-hexane. The structural formula is shown below.
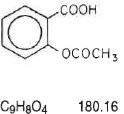
The aspirin component is 2-(acetyloxy)-, Benzoic acid, a white crystal, commonly tabular or needle-like, or white, crystalline powder. Is odorless or has a faint odor. Is stable in dry air; in moist air it gradually hydrolyzes to salicylic and acetic acids. Slightly soluble in water; freely soluble in alcohol; soluble in chloroform and in ether; sparingly soluble in absolute ether and is represented by the following structural formula:
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Methocarbamol and Aspirin provides a double approach to the management of discomforts associated with musculoskeletal disorders.
Methocarbamol
The mechanism of action of methocarbamol in humans has not been established, but may be due to general central nervous system depression. It has no direct action on the contractile mechanism of striated muscle, the motor end plate or the nerve fiber.
Aspirin
Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) works by inhibiting the body's production of prostaglandins, including prostaglandins involved in inflammation. Prostaglandins cause pain sensations by stimulating muscle contractions and dilating blood vessels throughout ..