What is the treatment?
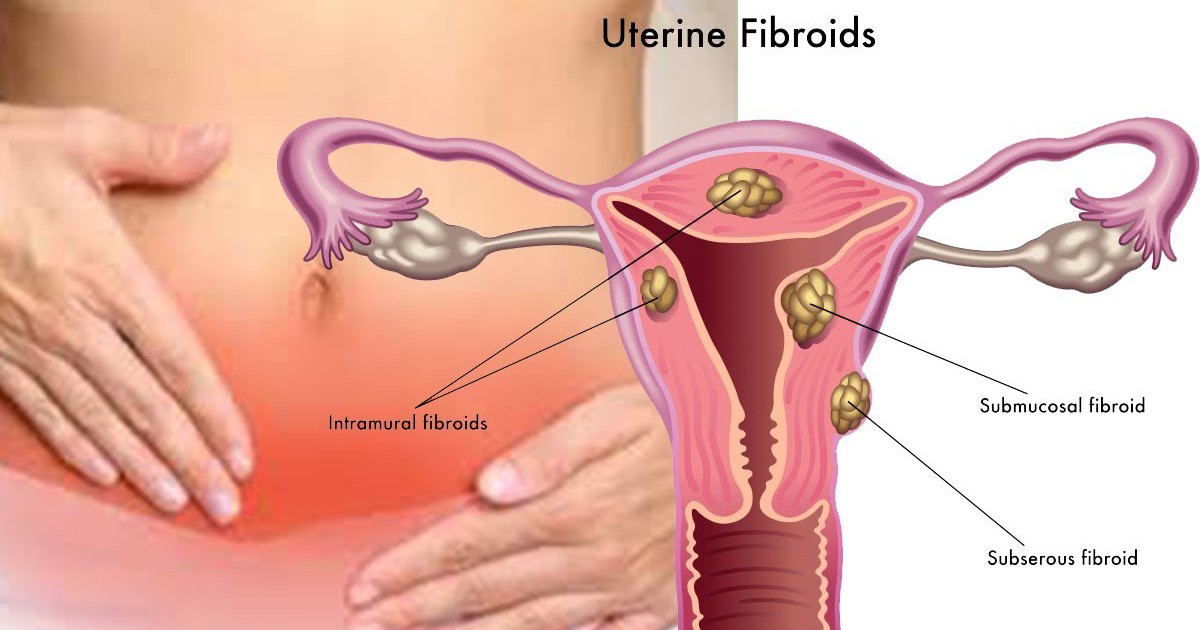
Uterine fibroids are firm, compact benign tumors which are made of smooth muscle cells and fibrous connective tissue that originate in the uterus (womb). Sometimes, these tumors become quite large and cause severe abdominal pain and heavy periods. Although it is not clearly known what causes fibroids, it is believed that each tumor develops from an aberrant muscle cell in the uterus, which multiplies rapidly because of the influence of the hormone estrogen.
Most women with uterine fibroids have no symptoms. But these fibroids can also cause a number of symptoms depending on their size, location within the uterus, and how close they are to adjacent pelvic organs. Symptoms of uterine fibroids may include heavy or prolonged menstrual periods, abnormal bleeding between menstrual periods, pelvic pain due to the pressure caused as the tumor presses on pelvic organs, frequent urination, low back pain, pain during intercourse etc. In most cases, these heavy or prolonged menstrual periods, or the abnormal bleeding between periods, can lead to iron-deficiency or anaemia in women.
After uterine fibroids has been diagnosed properly relating its size, location etc. the patient may receive a combination of treatments. The doctor may prescribe medicines to destroy the fibroids. In case the fibroids are large and multiple, surgeries (myomectomy) may be performed. The doctor may also perform a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) if the condition worsens, or if no other treatments work. Also, a new and completely non-invasive surgical procedure can be performed. This is called forced ultrasound surgery (FUS) where high-energy, high-frequency sound waves are directed at the fibroids to destroy (ablate) them.
How is the treatment done?
Fibroids are not cancerous nor do they interfere with pregnancy. In such instances, women can get along with it without any treatment. They tend to shrink after menopause, when levels of reproductive hormones drop. But, otherwise, in order to treat uterine fibroids, medications are prescribed to regulate the menstrual cycle, treating symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding and pelvic pressure. These medicines like Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (Gn-RH) agonists, Progestin-releasing intrauterine device (IUD) target the hormones and thus help to shrink the fibroids. Non -steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which may be taken side by along with the other medicines, may be effective in relieving pain related to fibroids.
MRI-guided focused ultrasound surgery (FUS) is a noninvasive treatment option for uterine fibroids that preserves the uterus. A high-energy ultrasound transducer detects the precise location of the uterine fibroids and sound waves (sonications) are used to heat and destroy small areas of fibroid tissue. Also, small particles (embolic agents) can be injected into the arteries supplying the uterus. This helps to cut off blood flow to fibroids, causing them to shrink and die. Laparoscopic procedures like myolysis and robotic myomectomy can also be used.
In case of multiple fibroids, very large fibroids or very deep fibroids, the doctor decides to perform surgical operations to remove the uterine fibroids. An open abdominal surgical procedure can help relieve the pain but affect future fertility. Also, hysterectomy can be performed as a permanent procedure. This involves removal of the uterus and ends one’s ability to bear children.
Who is eligible for the treatment? (When is the treatment done?)
Usually, uterine fibroids do not cause much trouble unless large. A patient should, nonetheless, consult a doctor if she has symptoms of fibroids which include irregular and heavy menstrual bleeding, bleeding between periods, pelvic or abdominal pain, frequent painful urination, or an inability to control the flow of urine, increasing abdominal girth etc. These symptoms of vaginal bleeding is also associated with dizziness, lightheadedness, shortness of breath, or chest pain
Who is not eligible for the treatment?
Unless women have bothersome or severe symptoms, they do not need to treat uterine fibroids. Doctors examine the changes and size of fibroids when one is pregnant to avoid any complication.
Are there any side effects?
Myomectomy poses a unique set of side effects. Risks may include infection of the pelvic region including uterus, fallopian tubes, or ovaries, scar tissue, injuries to the bladder or bowel. As a result of fibroids, the person might already have lost blood. Surgical operations may cause further complications like blood loss, infertility etc. Also, such operations if carried out callously, can increase the risk factors of having cancer.
What are the post-treatment guidelines?
After treatment, all patients should follow their health care practitioner's instructions. A health care practitioner or doctor may choose to perform more frequent pelvic exams, such as every six months, to determine whether there has been additional growth of fibroid tissues or other complications.
How long does it take to recover?
Time to recover depends on the size of the fibroids and the procedure of treatment. Medications may take a longer time to gradually cut down on the tissues and fiber growths. Surgical operations also provide variable recovery time. Hysteroscopy is an outpatient procedure and requires from a few days to 2 weeks to recover. Laparoscopy requires 1 to 2 weeks. Laparotomy is a longer procedure and may require 4 to 6 weeks to recover.
Are the results of the treatment permanent?
Use of medications like Gonadotropin releasing hormone agonists (GnRHa) and others do not guarantee a permanent cure. There may arise issues relating pregnancy or recurrent pregnancy loss related to submucosal fibroids. The only permanent solution for uterine fibroids is undergoing surgical operations. Complete removal of uterus provides permanent relief from extreme symptoms of fibroids but also take away the ability to become pregnant.
What are the alternatives to the treatment?
Homeopathy is a lot more effective treatment of uterine fibroids. Though slowly, but homeopathy provides the best non surgical treatment for fibroids. The medicines surely retard the growth of fibroids and over a period of time, the fibroids disappear completely. This is a far more effective and the most convenient treatment of fibroids.
There is no specific self-care is available for uterine fibroids. In case of immense pain, women may apply heat to the lower abdomen by using a heating pad or hot water bottle. Doing exercise, which improves blood flow, may also reduce pain. Anemia can be prevented by Increasing the amount of iron in the diet.