Chicken Pox: Facts You Should Know
Chickenpox is caused by a virus called varicella zoster. Infection occurs after coming in contact with an infected person. It is the most infectious diseases. This virus is contagious to those around you for one or two days before your blisters appear. Varicella zoster viruses are contagious until all blisters get crusted.
-
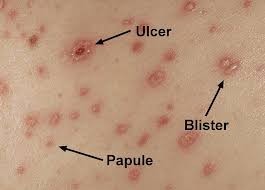
Itchy, red rash is the classic sign of chickenpox: extremely itchy, blistery red rash that typically starts on the face and trunk spreading to the rest of the body, progressing from red bumps to fluid-filled blisters to scabs. Other symptoms are fever, headache and fatigue.
-
It is highly contagious: spreads easily through the air when a person with the virus sneezes or coughs. Can also spread by touching the fluid from the blisters. An infected person is contagious from 1 to 2 days before he gets the rash all his blisters have formed scabs. Once exposed, it takes between 10 to 21 days to develop chickenpox.
-
It is usually mild but can be very serious: Mostly mild but in some cases, it can lead to serious complications such as dehydration, pneumonia, bleeding, encephalitis, bacterial skin infections, toxic shock syndrome and bone and joint infections. Certain groups, including infants, teens, adults, pregnant women, and people with weakened immune systems due to illness or medications are at higher risk of complications.
-
Vaccine is your best defence against the defence: the ‘’total efficacy’’ rate is between 80 to 85 percent and in virtually 100 percent of cases it will prevent serious illness in otherwise healthy individuals. For the best protection, children (and adults) need two doses of the vaccine.
-
You can usually manage your child’s symptoms at home: Acetaminophen relieves fever, Oatmeal baths and calamine lotion can help lessen the itchiness, and Acyclovir can reduce the symptoms but is usually given in certain circumstances.
-
Once someone has chickenpox, he probably won't get it again-but he could get a related disease called Shingles: After chickenpox, the varicella zoster virus that causes it remains in the body in an inactive state. The virus reactivates years later, causing Shingles. The risk increases with age. Shingles vaccine is recommended for age 60 or older.
What are the Typical Signs or Symptoms of Chickenpox?
Signs and symptoms of chicken pox includes :
-
Fever
-
Loss of Appetite
-
Headache
-
Tiredness and a general feeling of being unwell(malaise)
Once the rash appears, it goes through three phases:
-
Raised red bumps with breakouts after couple of days
-
Small fluid-filled blisters which later break and leak
-
Crusts and scabs cover the blisters and take several days to heal.
New bumps continue to appear for several days and so all three phases-bumps, blisters and scabs appear at the same time. In severe cases, the rash may spread all over the body and lesions may form in throat, eyes, mucous membranes of urethra, anus and vagina. It is very itchy and can make children feel miserable even if not too serious and it is usually much worse in adults.
What are the Causes of Chickenpox?
Chicken Pox caused by a virus called varicella zoster. Infection occurs after coming in contact with an infected person. It is the most infectious diseases. This virus is contagious to those around you for one or two days before your blisters appear. Varicella zoster viruses are contagious until all blisters get crusted. The virus can spread through:
-
Saliva
-
Coughing
-
Sneezing
-
contact with fluid from the blisters
Anyone who has not been exposed may contract the virus. Risk increases when:
-
You had recent contact with an infected person
-
You are under 12 years of age.
-
You are an adult living with infected children
-
You have spent time in school or child-care facility with infected cases.
-
Your immune system is compromised due to illness or medications.
How to Stop Chickenpox from Spreading on the Body?
The procedure to stop chicken pox from spreading all over the body are as follows:
-
Keep children off nursery or school until all the spots have crusted over.
-
Keep the nails trimmed to avoid bursting the blisters.
-
Apply calamine lotion to help reduce itching.
-
Wear mittens to prevent scratching.
-
Serve sugar-free popsicles to soothe mouth sores which appear as a result of lesions in the mouth which are very painful.
-
Bath in Oatmeal: soothing and itch-relieving.
-
Take baking soda baths: itch-relieving.
-
Use chamomile compresses: antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects.
What are the Ways for Chickenpox Diagnosis?
The chicken pox is mostly diagnosed first and foremost by the distinctive rash.
-
Blood test: If you or your child has been exposed to chickenpox, your doctor may order a test to see if you or they are already immune from chicken pox. This is called the immunity test. This is a blood test that checks whether you are producing the antibodies to the virus. If the test shows antibodies, you will be naturally protected from the virus. If you don't have the antibodies, then you will need to be monitored closely to see if you develop symptoms.
-
Viral culture: sometimes a culture is done instead of a blood test .A sample of fluid is taken from the blister and sent to the lab, where the specimen is allowed to grow. After a period of time, it’s checked for the varicella-zoster virus. Results of this won't come back until the virus has already run its course.
What is Chickenpox Treatment?
Chicken pox Treatment in Children:
-
If you or your child is at high risk of developing complications of chickenpox, doctors may prescribe acyclovir or intravenous immunoglobulin. These may lessen the severity of chicken pox if given within 24 hours of developing the rash first.
-
In some cases, vaccine maybe suggested after exposure to prevent or lessen the severity.
-
Antibiotics may be prescribed for skin infections and pneumonia. Encephalitis may be treated with antiviral drugs. Hospitalisation is usually necessary.
-
Avoid scratching: Put gloves on his/her hands at night especially. Also trim their nails.
-
Relieve the itch and other symptoms: cool bath with added baking soda, aluminium acetate, uncooked oatmeal.
-
Apply calamine lotion dabbed on the spots.
-
Antihistamines like diphenhydramine for itching.
-
Acetaminophen for fever.
-
Isolating the child in avoiding the spread of the infection.
Chicken pox Treatment in Adults
Chickenpox symptoms in adults typically resemble those in children, but they can become more severe. The treatment includes:
-
Calamine lotion dabbed on the spots
-
Colloidal oatmeal baths to relieve itching
-
Medicines : a pain reliever, medicine to reduce fever and antibiotics for controlling infection.
-
In some cases, vaccine maybe suggested after exposure to prevent or lessen the severity.
-
Isolation to avoid spreading of infection.
What Food to Eat and What to Avoid During Chicken Pox?
Foods to Avoid:
-
Salty foods - They may a sore mouth and may worsen issues such as dehydration.
-
Fatty foods - Foods high in saturated fat cause inflammation which can slow the healing of the irritated area.
-
Spicy foods - They irritate the oral sores.
Foods to Eat:
-
Juices and tea: Loss of appetite is common in these patients leading to dehydration and so immunity-boosting juices are helpful in this. Other drinks are cinnamon, chamomile and basil herbal teas to boost immune system.
-
Fruits: Those with immune-boosting vitamin C are the best for affected individuals. But if the patient has blisters in the mouth, avoid fruits with acidic juices as they cause irritation and pain.
-
Ice-lollies: soothing to the oral ulcers.
How to Prevent Chickenpox Naturally?
Ways of preventing the chicken pox naturally:
-
Keeping immunity strong: by getting enough sleep, eating healthy foods, doing exercise, quitting exercise, practicing good hygiene and taking dietary supplements.
-
Avoid adults and children with chickenpox: Sequestering your affected child in their room while keeping them well fed and hydrated and keeping them off schools or nursery, making them wear a mask, keeping their nails trimmed.
-
Disinfect your house and hands: Regularly disinfecting counter tops, tables, arms of chairs, toys and other surfaces which may have come in contact with an infected person is a good preventive measure. Giving over a bathroom solely to the infected person while he is ill must be considered. Also disinfecting hands repeatedly by washing them with soap. Also using natural disinfectants like vinegar, lemon juice, and salt, diluted hydrogen peroxide, etc. is also very important rather than using synthetic ones. Making sure all the linen used by an infected individual is properly cleaned and disinfected is necessary. Never rub mucus membranes after touching an infected person.
-
Using natural anti-viral compounds as supplements like vitamin C, olive leaf extract, garlic, oregano oil, colloidal silver.