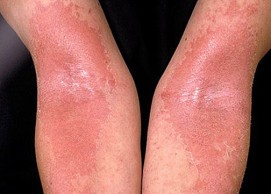
What is Eczema?
In eczema condition, skin patches turn inflamed, red, itchy, cracked and rough. Some people develop blisters. The United States holds a high ratio of eczema people. There are different types and stages. Eczema specifically talks about Atopic Dermatitis which is the most common type of eczema.
Atopic means a group of ailments involving the immune system, including atopic dermatitis, hay fever and asthma. Dermatitis is the inflammatory condition of the skin.
For most infants, this condition outgrows in their tenth year whereas some people continue to have symptoms on and off throughout their life. People with proper treatment can have good control over the disease. Living with eczema is really challenging and it can range from mild, moderate to severe.
Eczema develops on the cheeks and chin in infants, but it can appear anywhere in the body. Even adults can develop with this condition even though it was not from their childhood.
Types of Eczema:
-
Allergic contact dermatitis (eczema) - A skin reaction which occurs with contact to a foreign substance.
-
Contact eczema - This occurs when the skin comes into contact with a certain allergen.
-
Dyshidrotic eczema - Irritation of the skin on the soles of the feet and palms and is characterized by tiny blisters.
-
Neurodermatitis - Scaly and itchy patches on the lower legs, wrists, forearms and hands.
-
Nummular Eczema - Circular patches which are itchy, scaly and crusty.
-
Seborrheic Eczema - Yellowish, scaly and oily ptches of skin occur on the face and scalp.
-
Stasis Dermatitis - This disorder is usually related to circulatory problems and is characterized by skin irritation on the lower legs.
What are the Symptoms of Eczema?
It is important to remember that eczema and its symptoms differ from person to person. There are some common symptoms of eczema as followed:
-
The very first symptom is intense itching
-
Later, the rash appears with redness, develops with bumps of different sizes
-
The itches may have a burning sensation, especially in thin skin like eyelids
-
It may start oozing and become crusty when scratched
-
Prolonged rubbing causes thickened plaques in the skin in adults
-
Over time, painful cracks may appear
-
The scalp problem may be rarely involved
-
Eyelids will turn itchy, puffy and reddish
-
The itching sensation may disturb the sleep pattern
-
Fungal infections such as ringworm, viral infections such as herpes and molluscum contagiosum are more common symptoms in people with eczema
What is the Main Cause of Eczema?
The exact cause of eczema is not known yet. Atopic dermatitis is the most common type resembles an allergy whereas the skin irritation is higher in children than in adults which is not an allergic reaction. However, the combined factors that cause eczema is found to be
-
Abnormality in the immune system
-
Genetic factors
-
Defects in the skin that allows germs in and moisture out
-
Activities that make the skin to be more sensitive and the environment
-
A poor skin barrier allows irritants, allergens, viruses and bacteria easily
-
The skin’s barrier ability becomes diminished when eczema affects a person
How to Prevent Eczema?
Some of the ways through which eczema can be prevented are as follows: Intense perspiration and overheat can trigger eczema outbreaks. Avoid heat environment and keep your bedroom always cool.
-
Stress may increase outbreaks. Do physical exercises, yoga, meditation to avoid stress and stay relaxed
-
Do not scratch the skin, gently rub the itching area
-
Wear comfortable clothes especially choosing cotton dress allows your body to breathe well
-
Do not expose to irritants and allergens
-
Try to take a bath in lukewarm rather than hot water
-
Use a mild soap for bath and pat the skin instead of rubbing
-
Drink at least eight glasses of water that keeps your skin moist
-
Use mild moisturizers
What is the Way For The Diagnosis of Eczema?
-
A detailed medical history will help to diagnose eczema. Besides, additional tests support the atopic dermatitis diagnosis.
-
Blood Test: In this test, eosinophils levels & IgE antibody will be checked out. Generally, atopic dermatitis and eczema people will have elevated levels of eosinophils and IgE.
-
Skin Biopsy: Small pieces of skin is removed and tested for other diseases such as low-grade skin cancer or psoriasis other than atopic dermatitis.
-
Buccal swabs: Tissues are swabbed from inside of the cheek with a cotton applicator to obtain cells as a DNA source material to trace out for mutations in the filaggrin gene, one of the main causes of eczema.
Other than the above, patch testing, skin allergy testing will be done from time to time.
What is the Best Treatment For Eczema?
-
Eczema treatment is provided with four goals such as controlling the itch, healing the skin, preventing flares and preventing infections. The treatment depends on the age, medical history and how bad the symptoms are.
-
Creams with hydrocortisone steroids help in relieving itching and reducing inflammation. They are available in different strengths from the OTC to the prescription medicines.
-
NSAID ointment is a new prescription non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory drug that is used to treat mild to moderate eczema. It is advised to apply twice a day and it is effective in reducing inflammation and helping the skin return to normal appearance.
-
Antibiotics are prescribed to treat bacterial infections caused by scrubbing the skin. Antihistamines help in relieving itching symptoms during the night time.
-
Drugs help in reducing immunity such as cyclosporine, methotrexate, and mycophenolate mofetil and corticosteroid pills, shots, liquids are used to reduce the flare-ups and itching.
-
UV light therapy and PUVA therapy are also recommended.
What Foods to Avoid if You Have Eczema?
Though food directly does not get involved with the condition still, it flares up the symptoms. The common foods to avoid are soy, nuts, eggs, citrus, gluten, tomatoes, and dairy products since they seem to have allergic among the affected people. Preservatives and artificial ingredients also aggravate the symptoms and such foods will be high in Trans fats such as margarine, processed food.
High sugary items such as cakes, some smoothies, burgers induce the inflammation. People with dyshidrotic eczema should avoid nickel rich foods such as lentils, black tea, beans, shellfish, pears, green apples. It is always good to eat well-balanced food and avoid triggers whichever you personally feel.
How Can You Get Rid of Eczema Naturally?
Natural ways of treating eczema are as follows:
-
Licorice root extract shows a promising reduction of itching. Adding a few drops of coconut oil or itch cream gives extra benefits.
-
Foods rich in Omega 3 fatty acids help during the flare-up times to boost immune function and speed up the healing process.
-
Taking Vitamin E speeds up healing by reducing inflammation and the topical ointment relieves itching and prevents skin from scarring.
-
Taking Vitamin A rich food helps for skin improvement
-
Calendula cream heals skin cuts, burns and inflammation. It improves blood flow in the affected area, helps in hydrating the skin and fights against infection
-
Alternative treatments like hypnosis, acupuncture reduce stress and anxiety levels.