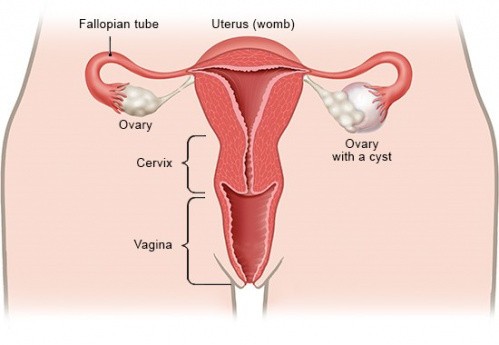
What is Ovarian Cysts?
Ovaries are the female reproductive system part, which located on both sides of the uterus in the lower abdomen. Ovaries produce eggs along with hormones estrogen and progesterone. Cysts is a fluid filled sacs, which is developed in one of the ovaries. In most of the cases, cysts don’t develop any symptoms and cause no pain. There various types of cysts such as dermoid cysts, endometrioma cysts, follicle, corpus luteum cysts and polycystic ovary syndrome which can cause infertility in woman.
Can ovarian cysts lead to cancer?
Ovaries are the organ located deep within the pelvis. In a maximum number of cases, cysts don’t develop any kind of pain. But cysts is something which has fluid and sac filled.
Fluid, follicle or tumor in the cysts doesn’t mean it lead to cancer. It is a kind of condition which affects almost every woman, ones in their life. But most of it doesn’t develop ovarian cancer.
What is the cause of Ovarian Cysts?
Ovarian Cysts are sacs filled with fluid, occurring in women mainly during their ovulation period. These Cysts commonly don’t have any symptoms and are usually harmless. The basic function of the ovaries is to produce an egg every month, this is called ovulation. During this time, a cyst like structure gets formed inside the ovary. This is known as a Follicle. The mature follicle fractures when an egg is released during ovulation. The empty follicle leads to the formation of a corpus luteum and, if pregnancy does not arise, the corpus luteum dissolve. Yet, sometimes, this process does not complete accordingly, lead to the most common type of ovarian cyst which is the functional ovarian cysts. Along with this, cysts can also occur because of reasons such as Endometriosis in which women suffering from endometriosis can flourish a type of ovarian cyst called an endometrioma and Severe pelvic infections which can spread to the ovaries or fallopian tube resulting in the formation of cysts.
What are the symptoms of Ovarian Cysts?
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Breast tenderness
-
Painful sex
-
Pelvic pain
-
Bloating
-
Inflammation
-
Lower back pain
What are the treatment of Ovarian Cysts?
The ovaries are part of the female reproductive system. They’re located in the lower abdomen on both sides of the uterus. Women have two ovaries that produce both eggs and progesterone and hormones estrogen.
Sometimes, a fluid-filled sac called a cyst will develop on one of the ovaries. Most of the women will grow at least one cyst during their lifespan. In most cases, ovarian cysts are painless and cause no conditions.
Treatment for an ovarian cyst are mentioned below:
The doctor may advise treatment to reduce the size or remove the cyst if it doesn’t go away on its own or if it grows further.
-
Birth control pills: If you have recurring ovarian cysts, the doctor may specify an oral contraceptive to stop ovulation and prevention for the development of new cysts. Oral contraceptives can also decrease your possibilities of ovarian cancer. The possibility of ovarian cancer is higher in postmenopausal women.
-
Laparoscopy: If your cyst is small in size and results from an imaging test to rule out cancer, the doctor can perform a laparoscopy to surgically remove the cysts. The method involves your doctor making a small incision close to your navel and then implanting a small instrument into your abdomen to remove the cyst.
-
Laparotomy: If you contain a large cyst, your doctor can surgically remove the cyst through a large incision in your abdomen. apart from this, they will conduct an urgent biopsy, and if they determine that the cyst is cancerous, they may perform a hysterectomy to remove your ovaries and uterus.
What are the post-treatment guidelines for Ovarian Cysts?
Treatment of ovarian cysts depends on various factors, such as the size and type of cyst, the woman's age and general well being, future pregnancy intentions of the patient. The earlier these cysts are observed, the less difficult the treatment would be. In some cases, the ovarian cysts do not require any treatment. In a postmenopausal patient, a repeated simple cyst smaller than 10 cm in size, along with the presence of a normal CA125 value may be followed with serial ultrasonographic examinations. If the cysts are less than 5 cm in size, no further investigation is required and there is no risk. If the size is 5-7 cm, these ovarian cysts detected in premenopausal women are functional and most of the functional cysts will have resolved within 2 months. Therefore, an ultrasound should be repeated at 6 months, with CA 125 only if a cyst is still there. CA 125 is not required at present. Non-functional benign cysts usually
remain unchanged.
What are the Side effects of Ovarian Cysts treatment ?
Most ovarian cysts are benign and go away on their own without the proper treatment. These cysts cause little if any, symptoms. But in some cases, doctors may discover a cancerous cystic ovarian mass during a periodic examination.
Ruptured cysts, can cause intense pain and bleeds internally. This complication the risk of an infection and can be very dangerous if not treated.
Ovarian torsion is another severe complexity of the ovarian cysts treatment. This is when a large cyst causes an ovary to twist or move from its own original state. Blood supply to the ovary is cut off, and if not treated, it can cause injury or death to the ovarian tissue. apart from this, exceptional, ovarian torsion reports for nearly 3 percent of emergency gynecologic surgeries.