Ethmozine
Generic name: moricizine hydrochloride
Dosage form: Tablets
Drug class:Group I antiarrhythmics
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jul 22, 2021.
On This Page
Ethmozine Description
Ethmozine® (moricizine hydrochloride) is an orally active antiarrhythmic drug available for administration in tablets containing 200 mg, 250 mg and 300 mg of moricizine hydrochloride. The chemical name of moricizine hydrochloride is 10-(3-morpholinopropionyl) phenothiazine-2-carbamic acid ethyl ester hydrochloride and the structural formula is represented as follows:
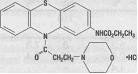
Moricizine hydrochloride is a white to tan crystalline powder, freely soluble in water and has a pKa of 6.4 (weak base). Ethmozine® tablets contain: lactose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium starch glycolate and dyes (FD&C Blue 1, D&C Yellow 10 and FD&C Yellow 6 [200 mg tablet]; FD&C Yellow 6 and F&C Red 40 [250 mg tablet]; FD&C Blue 1 [300 mg tablet]).
Ethmozine - Clinical Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Ethmozine® is a Class I antiarrhythmic agent with potent local anesthetic activity and myocardial membrane stabilizing effects. Ethmozine® reduces the fast inward current carried by sodium ions.
In isolated dog Purkinje fibers, Ethmozine® shortens Phase II and III repolarization, resulting in a decreased action potential duration and effective refractory period. A dose-related decrease in the maximum rate of Phase 0 depolarization (Vmax) occurs without effect on maximum diastolic potential or action potential amplitude. The sinus node and atrial tissue of the dog are not affected.
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology studies in patients with ventricular tachycardia have shown that Ethmozine®, at daily doses of 750 mg and 900 mg, prolongs atrioventricular conduction. Both AV nodal conduction time (AH interval) and His-Purkinje conduction time (HV interval) are prolonged by 10-13% and 21-26%, respectively. The PR interval is prolonged by 16-20% and the QRS by 7-18%. Prolongations of 2-5% in the corrected QT interval result from widening of the QRS interval, but there is shortening of the JT interval, indicating an absence of significant effect on ventricular repolarization. Intra-atrial conduction or atrial effective refractory periods are not consistently affe...



